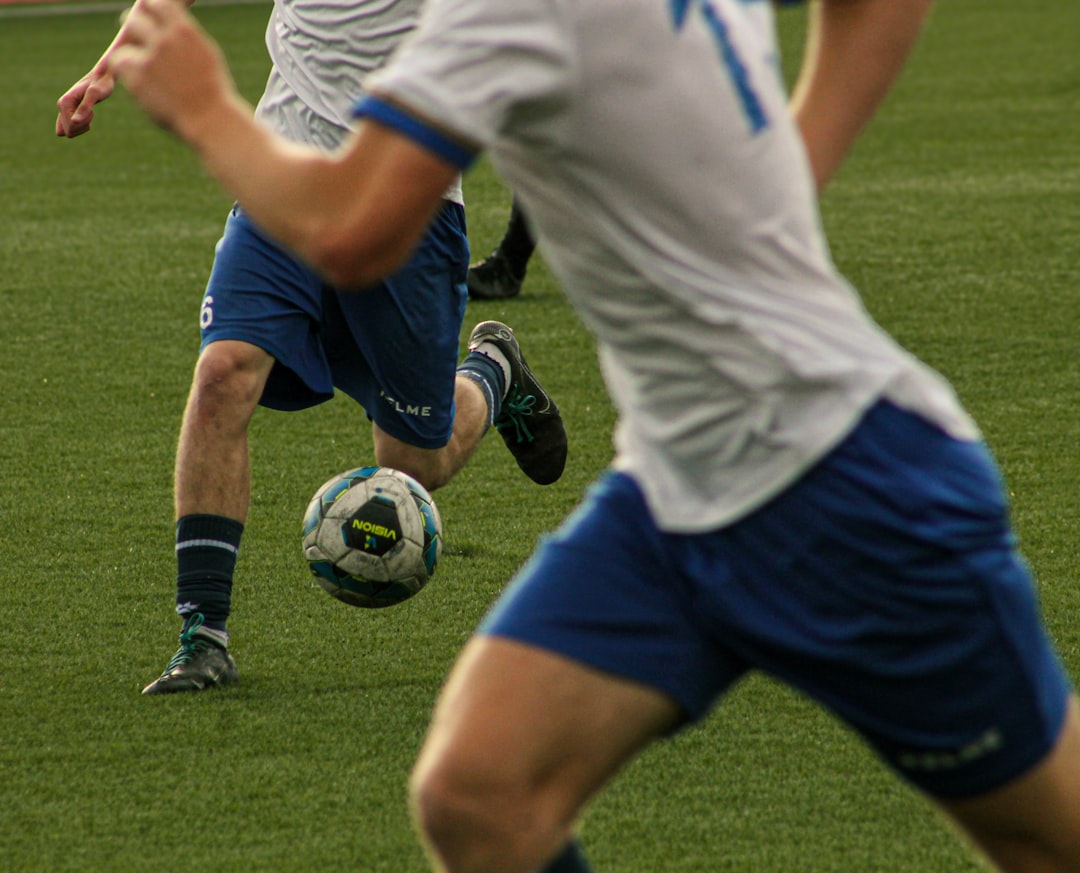
In the high-energy world of soccer, nutrition plays a critical role in performance, endurance, and recovery. Soccer players in America—whether amateur, collegiate, or professional—need diet plans that fuel their intense training schedules and competitive matches. With the sport demanding agility, speed, and stamina, tailored nutrition becomes essential to maintain peak performance across all levels of play.
So, what are the best diet plans for soccer players in America? These plans emphasize whole foods, proper hydration, and strategic timing of meals. Let’s dive into what makes a good diet plan for soccer stars and how it can be customized based on individual needs.
Key Nutritional Goals for Soccer Players
Before selecting a specific diet plan, it’s important to understand the core nutritional goals that athletes in this sport should strive for:
- Energy Provision: Soccer players need carbohydrates for quick and sustained energy.
- Muscle Maintenance: Protein intake supports muscle repair and growth, especially after intense activity.
- Hydration: Regular fluid intake prevents cramping and supports focus and endurance.
- Recovery: Antioxidant-rich foods support faster recovery and reduce inflammation.
1. The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is often recommended for its balanced, heart-healthy approach that blends moderation with high-quality ingredients. For soccer players, this diet supports sustained energy and reduces inflammation post-training.
- Emphasis on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats like olive oil
- Lean protein sources including fish, chicken, and legumes
- Minimal processed foods and refined sugars
This plan is ideal for soccer players looking to improve their overall health while maintaining performance-enhancing energy levels.
2. High-Carb, High-Protein Soccer Meal Plan
A high-carbohydrate, high-protein plan is tailored specifically for athlete performance. Carbs are essential for pre-match energy, while proteins aid in muscle repair post-match.
Sample daily meal outline:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and Greek yogurt
- Lunch: Brown rice, chicken breast, and mixed vegetables
- Snack: Banana with almond butter or a protein shake
- Dinner: Whole wheat pasta with lean ground turkey and tomato sauce
- Hydration: Water throughout the day, with electrolyte drinks post-training
This approach is especially beneficial during training seasons or match-heavy weeks when energy and recovery are top priorities.
3. Plant-Based Athlete Diet
Plant-based diets are gaining popularity among athletes, including soccer players. With the right planning, plant-based nutrition can support high-level performance while improving overall health.
Essential components of a plant-based soccer diet:
- High-protein legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Nutritional yeast, tofu, and tempeh for muscle support
- Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice for energy
- Plenty of colorful fruits and vegetables
- Omega-3 fats from flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts

Many soccer players choose this diet for its anti-inflammatory benefits and lighter digestion, which helps them stay agile and focused on the pitch.
Timing and Pre-Match Nutrition
Timing is just as important as content when it comes to fueling a soccer player. Eating large meals right before a match can lead to digestive discomfort and sluggishness. Ideally, players should:
- Consume a carbohydrate-rich meal 3–4 hours before a match
- Add a light snack like a banana or an energy bar 1 hour before kickoff
- Hydrate properly the day before and continue sipping liquids in the hours leading up to the game
Post-match nutrition should include a mix of carbs and protein within 30–60 minutes of finishing to begin the recovery process.
Hydration: The Often-Overlooked Element
Many players forget that even slight dehydration can decrease cognitive and physical performance. In America’s diverse climates—from the heat of the South to cooler Northern states—hydration needs can vary.
- Drink water consistently throughout the day, not just during games
- Include electrolyte-enhanced beverages during long matches or hot weather
- Monitor urine color as a hydration indicator—it should be pale yellow
Supplements: When Diet Needs a Boost
While whole foods should be the foundation of any athlete’s diet, some players may benefit from supplements such as:
- Whey or plant-based protein powders for convenient recovery nutrition
- Creatine for increased athletic output and faster recovery
- Multivitamins to address any nutritional gaps
- Omega-3 capsules if not consumed naturally
Always consult a sports nutritionist or physician before adding new supplements to your regimen.
Conclusion
The best diet plan for a soccer player depends on their personal health, goals, and playing schedule. Whether following a Mediterranean, high-carb, or plant-based plan, the focus should always be on quality, timing, and hydration. With the right diet, soccer players in America can unlock optimal performance and longevity in their athletic careers.



